Difference between revisions of "Main Page"
| (14 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
| + | |||
[[Image:Opening_picture_on_homepage_source_TomBuijse.jpg|680px]] | [[Image:Opening_picture_on_homepage_source_TomBuijse.jpg|680px]] | ||
| − | |||
| + | =REFORM river restoration wiki= | ||
| + | '''Guidance and tools for hydromorphological assessment and physical restoration of rivers and streams in Europe''' | ||
| + | <br /> | ||
| + | |||
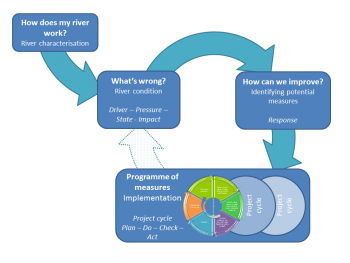
| + | [[File:Base_structure_wiki_total.PNG|thumb|350px|right|link=What's_in_this_wiki?|What's in this wiki? Click image to start.]] | ||
== Hydromorphology and river restoration == | == Hydromorphology and river restoration == | ||
| − | |||
Flowing water, inundation, erosion, sedimentation ... These are key processes for river and floodplain ecosystems from the realm of hydromorphology. Yet the European Water Framework Directive pays little attention to hydromorphological processes. That is why the European Commission funded the REFORM project for improving the success of hydromorphological restoration measures. This wiki guides the practitioner along the results. | Flowing water, inundation, erosion, sedimentation ... These are key processes for river and floodplain ecosystems from the realm of hydromorphology. Yet the European Water Framework Directive pays little attention to hydromorphological processes. That is why the European Commission funded the REFORM project for improving the success of hydromorphological restoration measures. This wiki guides the practitioner along the results. | ||
== Why this wiki? == | == Why this wiki? == | ||
Successful river restoration calls for understanding the complex systems of hydromorphology and ecology. Processes operate at different scales, different disciplines play a role, and different species depend on hydromorphology in different ways. River restoration practitioners face the challenge of finding their way in this complexity when developing an integrated design. This wiki provides them with guidance. It structures the information along the different stages of restoration projects and river basin management plans. It offers quick access to key information, with links to deeper background information ranging from case-study experiences to scientific publications. | Successful river restoration calls for understanding the complex systems of hydromorphology and ecology. Processes operate at different scales, different disciplines play a role, and different species depend on hydromorphology in different ways. River restoration practitioners face the challenge of finding their way in this complexity when developing an integrated design. This wiki provides them with guidance. It structures the information along the different stages of restoration projects and river basin management plans. It offers quick access to key information, with links to deeper background information ranging from case-study experiences to scientific publications. | ||
| − | <br /><br /> | + | <br /> |
| − | + | <br /> | |
| − | ''' | + | '''Click [[River_basin_management_plan|What's in this wiki?]] to start or click on any of the menu items on the left.''' |
| − | + | <br /> | |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
| − | <p> The REFORM web-based tool is a knowledge and information system relating hydromorphology and ecology of European rivers and has been developed as part of the projects [http://www.reformrivers.eu/ REFORM] and [[Forecaster_Description|FORECASTER]] funded by the European Commission, [http://www.iwrm-net.eu/ IWRM-Net] and [http://www.delftcluster.nl/ Delft Cluster].</p> | + | <p>''The REFORM web-based tool is a knowledge and information system relating hydromorphology and ecology of European rivers and has been developed as part of the projects [http://www.reformrivers.eu/ REFORM] and [[Forecaster_Description|FORECASTER]] funded by the European Commission, [http://www.iwrm-net.eu/ IWRM-Net] and [http://www.delftcluster.nl/ Delft Cluster].''</p> |
<br /> | <br /> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:26, 18 December 2015
REFORM river restoration wiki
Guidance and tools for hydromorphological assessment and physical restoration of rivers and streams in Europe
Hydromorphology and river restoration
Flowing water, inundation, erosion, sedimentation ... These are key processes for river and floodplain ecosystems from the realm of hydromorphology. Yet the European Water Framework Directive pays little attention to hydromorphological processes. That is why the European Commission funded the REFORM project for improving the success of hydromorphological restoration measures. This wiki guides the practitioner along the results.
Why this wiki?
Successful river restoration calls for understanding the complex systems of hydromorphology and ecology. Processes operate at different scales, different disciplines play a role, and different species depend on hydromorphology in different ways. River restoration practitioners face the challenge of finding their way in this complexity when developing an integrated design. This wiki provides them with guidance. It structures the information along the different stages of restoration projects and river basin management plans. It offers quick access to key information, with links to deeper background information ranging from case-study experiences to scientific publications.
Click What's in this wiki? to start or click on any of the menu items on the left.
The REFORM web-based tool is a knowledge and information system relating hydromorphology and ecology of European rivers and has been developed as part of the projects REFORM and FORECASTER funded by the European Commission, IWRM-Net and Delft Cluster.