Difference between revisions of "KUIVAJOKI"
(→KUIVAJOKI) |
(→Drivers, Pressures, Measures) |
||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
==Site description== | ==Site description== | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
=Drivers, Pressures, Measures= | =Drivers, Pressures, Measures= | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 10 June 2015
KUIVAJOKI
Key features of the case study
River Kuivajoki is a mid-sized lowland boreal river, with 970 km2 catchment area. The river is 46 km long and descends 89 metres from Lake Oijärvi to Bothnian Bay, northern part of the Baltic Sea.
Lake Oijärvi is regulated for flood protection and for recreational use. From Lake Oijärvi, River Kuivajoki flows first 4 kilometers in two channels: in a natural channel and in an artificial regulation channel. At the upper part of the natural channel there is a submerged weir which may prevent fish migration during low water level. At the upper end of the regulation channel, there is a dam which is a migration barrier for fish.
River Kuivajoki is included in the Salmon Action Plan by International Baltic Sea Fishery Commission aiming to re-establish wild salmon population in the river. Kuivajoki is protected from hydropower construction by the Finnish Act on the protection of rapids.
Water quality of the river is deteriorated due to human activities in the catchment. The main pressures in are peat mining, forestry and agriculture and municipal point sources.
Site description
Drivers, Pressures, Measures
Fast-flowing riffle sections in Kuivajoki, as in most other Finnish rivers, were channelized to facilitate timber transport and for flood protection in early 1900s. Channelisation included removing boulders from the channel (Picture 3) which lead to loss of habitats and decreased heterogenity in stream flow patterns. Last timber was transported in Kuivajoki in 1954.
Restoration of channelised riffle sectionss started in Finland in 1970´s. Since then in total 2000 riffles and 1000 and breeding sites have been restored. The goals were to return the natural morphology of the streams and to create natural current conditions especially to enable breeding and migration of salmonid fish.
In Kuivajoki, altogether about 5 km of the river (consisting of multiple riffle sections in the river) were restored in early 2000s. The stream bottom was rearranged using boulders were removed from the channel and placed along stream margins during channelization. Also gravel beds were created to provide nursery habitat for salmonids. The funding for the restorations came from regional water boards.
Also the regulation of Lake Oijärvi has been developed to prevent the drying of the natural stream at upper parts of Kuivajoki (where Oijärvi flows to Kuivajoki) and to enable the migration of fish at all water levels.
Riffles in upper part of Kuivajoki river are still channelized. Kuivajoki was chosen as a REFORM case study because it is among the few rivers in Finland that still had non-restored degraded upstream control sites to meet the study design of REFORM WP4. Kalliokoski is one of the channelized riffle sites and it is the non-restored degraded control site in WP4 case study (Picture 2). Hirvaskoski is one of the riffle sections in River Kuivajoki where restoration measures were conducted and it is the restored site in WP4 case study (Picture 1).
 The restored riffle section Hirvaskoski at River Kuivajoki. Most of the boulders that were removed from the river during channelisation were placed back in early 2000s to create more heterogenous habitat for the stream biota.
The restored riffle section Hirvaskoski at River Kuivajoki. Most of the boulders that were removed from the river during channelisation were placed back in early 2000s to create more heterogenous habitat for the stream biota.
The non-restored riffles lack heterogenous flow pattern of the natural riffle sections.
During channelisation for timber transport boulders were removed from the river channel and placed at the banks where they still remain (photo from non-restored Hirvaskoski 2012).
Measures selection
Information can be found under "site description".
Success criteria
No information found.
Ecological response
Electrofishing was done at Kuivajoki at 13 sites in 2003 after the restorations. Both salmon (Salmo salar, frequency 10/13) and grayling (Thymallus thymallus, frequency 7/13) were caught. However, all salmon individuals were older than one year and the age class 0+ was missing which indicates that natural breeding may not happen. The catch had also perch (Perca fluviatilis, frequency 9/13) and roach (Rutilus rutilus, frequency 4/13). The fish showed good quality class in 2003. The results in 2003 were similar to results from years 1999-2007. In 2006-2009 28 fish sites were monitored. The monitoring indicated good status of the fish communities and no change to the previous results (EQR = 0,77). Macroinvertebrates from restored Hirvaskoski and Soininkoski were assessed to be in good quality class in 2006. Based on samples 2009 and 2012 Hirvaskoski was placed in status class high ( EQR = 0,843). Also periphyton indicated good quality status in 2006-2012 (EQR 0,67).
Water quality response
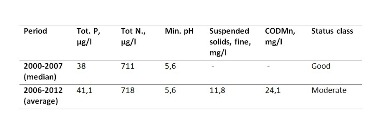
After the restorations (period 2000-2007) total phosphorus concentration, minimum pH and total nitrogen indicated good status. In 2006-2012 total phosphorus indicated moderate status, whereas minimum pH and nitrogen indicated good class. Water quality is degraded likely by eight peat mining areas and a wastewater treatment plant.
Hydromorphological response
No information found.
Monitoring before and after implementation of the project
Before-after monitoring of the restoration success was not done. However, assessment of the ecological and water quality status of River Kuivajoki has been done after the restorations.
Socio-economic aspects
No information found.
Contact person within the organization
Finnish Environmental Institute, Freshwater Centre
Jukka Aroviita
E-mail: jukka.aroviita@ymparisto.fi
Extra background information
References
Aronsuu K. & Isid D. 2010. Pohjois-Pohjanmaan jokien hydrologis-morfologiset muutokset sekä mahdolliset hydrologiaan ja morfologiaan vaikuttavat toimenpiteet jokien ekologisen tilan parantamiseksi, www.ymparisto.fi/oulujoen-iijoenvesienhoitoalue
The Finnish Environmental Information: Hertta database.
Vesien kunnostustyöryhmä. 2012. Vesien kunnostustyöryhmän loppuraportti.
http://www.hare.vn.fi/mAsiakirjojenSelailu.asp?h_iId=16574&a_iId=180254
Related Measures
- Improve water retention
- Add/feed sediment
- Ensure minimum flows
- Establish environmental flows / naturalise flow regimes
- Shallow water courses
- Add sediments
- Initiate natural channel dynamics to promote natural regeneration
- Reduce impact of dredging
- Recreate gravel bar and riffles
- Lower river banks or floodplains to enlarge inundation and flooding
- Other measures