Difference between revisions of "Manage dams for sediment flow"
(→Cost-efficiency) |
(→Manage dams for sediment flow) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
=Manage dams for sediment flow= | =Manage dams for sediment flow= | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
==General description == | ==General description == | ||
| + | Almost every reservoir is affected by sedimentation. The World Commission on Dams estimated that each year almost 1 % of worldwide storage capacity is lost due to this effect. Even the actual new build of reservoirs does not level out over-all storage decrease. Dredging and disposing reservoir sediment is extremely expensive. On the other hand the sediment which is missing downstream of reservoirs leads to erosion damages, substrate deficits and ground water problems. <br /> | ||
| + | [[File:Worldwide Reservoir Siltation small.png]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <small>(data source: Jolanda Jenzer, Giovanni De Cesare: Möglichkeiten und Anwendung einer Datenbank bezüglich der Stauraumverlandung von alpinen Speichern, Wasser Energie Luft, 2006, Heft 3)<br /></small> | ||
| + | |||
| + | When removing the sediments or even reducing the sediment volume in the reservoir of hydropower plants or other hydro facilities plant operators are faced with exorbitant costs of several million Euro range even for small reservoirs. Moreover, the various sediment removal procedures applied so far – flushing through the main valve, manual or sludge dredging – all have various additional negative secondary effects ranging from compromising the operation (up to plant shut down for several months), loss of huge quantities of water to negative morphological or ecological impacts. | ||
==Applicability == | ==Applicability == | ||
Revision as of 17:07, 19 March 2013
Contents
- 1 Manage dams for sediment flow
- 1.1 General description
- 1.2 Applicability
- 1.3 Expected effect of measure on (including literature citations):
- 1.4 Temporal and spatial response
- 1.5 Pressures that can be addressed by this measure
- 1.6 Cost-efficiency
- 1.7 Case studies where this measure has been applied
- 1.8 Useful references
- 1.9 Other relevant information
Manage dams for sediment flow
General description
Almost every reservoir is affected by sedimentation. The World Commission on Dams estimated that each year almost 1 % of worldwide storage capacity is lost due to this effect. Even the actual new build of reservoirs does not level out over-all storage decrease. Dredging and disposing reservoir sediment is extremely expensive. On the other hand the sediment which is missing downstream of reservoirs leads to erosion damages, substrate deficits and ground water problems.
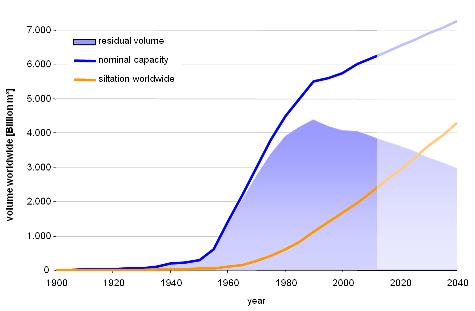
(data source: Jolanda Jenzer, Giovanni De Cesare: Möglichkeiten und Anwendung einer Datenbank bezüglich der Stauraumverlandung von alpinen Speichern, Wasser Energie Luft, 2006, Heft 3)
When removing the sediments or even reducing the sediment volume in the reservoir of hydropower plants or other hydro facilities plant operators are faced with exorbitant costs of several million Euro range even for small reservoirs. Moreover, the various sediment removal procedures applied so far – flushing through the main valve, manual or sludge dredging – all have various additional negative secondary effects ranging from compromising the operation (up to plant shut down for several months), loss of huge quantities of water to negative morphological or ecological impacts.
Applicability
Expected effect of measure on (including literature citations):
- HYMO (general and specified per HYMO element)
- physico � chemical parameters
- Biota (general and specified per Biological quality elements)
Temporal and spatial response
Pressures that can be addressed by this measure
- Reservoir flushing
- Artificial barriers upstream from the site
- Artificial barriers downstream from the site
- Impoundment
- Sedimentation and sediment input
Cost-efficiency
Direct sediment transfer cost should be about the same than pure suction dredging. However, the major cost share on dredging work is not the suction, but dewatering and deposition of the "surplus" sediment which often makes up 80 % of overall cost. On a global view, also from pure cost perspective sediment flow/transfer is much more efficient than sediment removal, saving 80 % expenditures and landfill in this example.