Difference between revisions of "Category:Vegetation Models"
m (→References) |
m (→Modelling Vegetation-Hydromorphology Interactions) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
=Modelling Vegetation-Hydromorphology Interactions= | =Modelling Vegetation-Hydromorphology Interactions= | ||
| − | Models can support river managers in the management, design and restoration of rivers. Here is summarised a review of modelling approaches that can help to investigate aspects of the interaction between plants and physical processes in river environments. The content is taken from section 3.4 of the Deliverable 2.2 (see also Solari et al. 2015). | + | Models can support river managers in the management, design and restoration of rivers. Here is summarised a review of modelling approaches that can help to investigate aspects of the interaction between plants and physical processes in river environments (see also [[:Category:Role_of_vegetation|Role of vegetation]]). The content is taken from section 3.4 of the Deliverable 2.2 (see also Solari et al. 2015). |
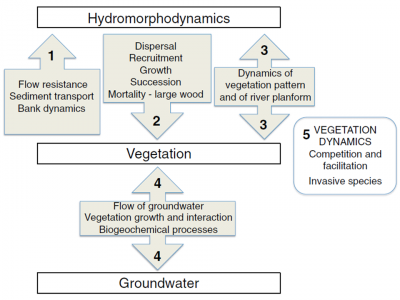
Models have been distinguished according to the following topics (Figure 1): | Models have been distinguished according to the following topics (Figure 1): | ||
Revision as of 15:58, 30 June 2015
Modelling Vegetation-Hydromorphology Interactions
Models can support river managers in the management, design and restoration of rivers. Here is summarised a review of modelling approaches that can help to investigate aspects of the interaction between plants and physical processes in river environments (see also Role of vegetation). The content is taken from section 3.4 of the Deliverable 2.2 (see also Solari et al. 2015).
Models have been distinguished according to the following topics (Figure 1):
(i) Effect of vegetation on hydromorphology. This includes the more complex models generally including advanced hydrology and sediment transport and simple vegetation which are mainly used for engineering purposes. It includes equations and process descriptions for flow resistance, bank erosion and bank accretion.
(ii) Effect of hydromorphology on vegetation. This includes ecological models using hydromorphodynamics as environmental variables influencing plant survival, growth, reproduction and dispersal.
(iii) Large wood. This includes models of breakage, transport and decomposition of large wood.
(iv) Interaction between vegetation and hydromorphology. This includes several models explicitly including the interaction between vegetation and hydromorphology (topics i and ii combined).
(v) Vegetation dynamics. This includes models that simulate interactions between plants and predict vegetation patterns in less disturbed environments (e.g. at higher altitudes on the floodplain) as a result of competition and facilitation processes.
(vi) Interaction between groundwater and vegetation. This includes ecohydrological models with vegetation dynamics.
For each topic are listed:
- the usability of the tools for the analysis of hydromorphological pressures and design of restoration measures;
- future research and modelling challenges.
References
Section 2.3 of the REFORM Deliverable 2.2 Part 1
Solari L., Van Oorschot M., Belletti B., Hebdrix D., Rinaldi M., Vargas-Luna A. (2015). Advances on modelling riparian vegetation-hydromorphology interactions. River Research and Applications. DOI: 10.1002/rra.2910
Pages in category "Vegetation Models"
The following 2 pages are in this category, out of 2 total.