Difference between revisions of "Rhine - Polder Altenheim"
(Created page with "=Rhine - Polder Altenheim= <googlemap version="0.9" lat="48.4665476791353" lon="7.77385711669922" zoom="13" width="100%" height="400" scale="yes" overview="yes" toc="no" cont...") |
(→Site description) |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
<Forecasterlink type="getProjectInfoBox" code="243" /> | <Forecasterlink type="getProjectInfoBox" code="243" /> | ||
| − | == | + | |
| + | ==General description== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Polder Altenheim is a 520 ha floodplain in the Upper Rhine (Rhine km 278 till 284) near the village of Altenheim. The floodplain has functioned as a controlled water retention area since 1987. Later, ecological flooding was introduced to restore the flood plain nature. 65 days per year river water is allowed to enter Polder Altenheim. It is now one of the oldest natural flood protection projects in Europe | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Pressures and Drivers== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The Upper Rhine suffers from hydrological regime modifications by artificial barriers upstream and downstream of Polder Altenheim. These barriers, along with channelization and embankments were built in order to control flooding of settlements in the floodplains of the Upper Rhine and for generating hydropower. The weirs now have a negative effect on the flood protection, since they impound the river blocking the discharge during high water events. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Global objectives== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The global objectives were two sided. First, the projects initial goal was to restore the flood water retention capacity of the Upper Rhine to pre-weir conditions. Later, the restoration of typical Rhine floodplain nature in Polder Altenheim was added as global objective. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Specific objectives== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The specific objectives for Polder Altenheim could not be found in the project documents and the question was not answered by the project manager in time. There are possible objectives for flood protection as well as some ecological targets concerning habitats, but this remains uncertain. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Success Criteria== | ||
| + | |||
| + | No success criteria were mentioned in the project documents. | ||
| + | |||
==Site description== | ==Site description== | ||
| + | |||
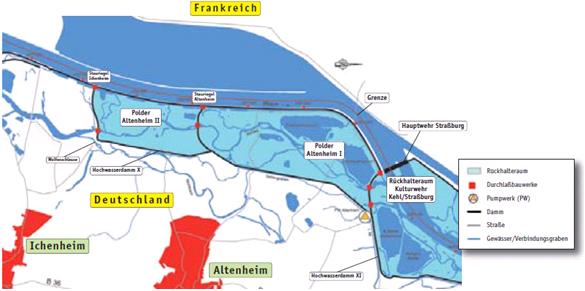
| + | [[File:Map polder altenheim.JPG ]] | ||
==Measures selection== | ==Measures selection== | ||
| − | + | To improve the water retention capacity while retaining a natural flooding frequency, two polders (Altenheim II and Altenheim I) are connected to the main river by a controlled inlet. These inlets are designed to flood parts of the polders 65 days per year. When there is a higher discharge of once per 10 years, the polders will automatically flood to increase the retention capacity of the river. The outlet of Polder Altenheim I is connected to the retention area, Kulturwehr Kehl/Straßburg. In the polder, the dynamics caused by the ecological flooding are allowed to shape the habitats. | |
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ==Monitoring== |
| − | + | ''Pre-restoration monitoring'' | |
| − | + | No evidence for pre-restoration monitoring could be found in the project documents | |
| − | == | + | ''Post-restoration monitoring'' |
| + | |||
| + | In 1993 till 1996, a large monitoring program was carried out in Polder Altenheim. In this program, the quantitative changes of reeds and forests, the number of species and presence of species of macro-invertebrates (Carabidae, land snails, spiders, grasshoppers, bees, female mosquitos), the number of caught fish, the number of caught individuals of birds, small mammals and amphibians and number of breeding pairs of birds, the total flooded area in different discharge scenarios and changes in characteristics of the soil and groundwater were measured from 1993 till 1996. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Expectations and Response== | ||
| + | |||
| + | It was expected that the ecological flooding regime has a positive effect on the floodplain habitats. The flood retention capacity of the Upper Rhine is enlarged and at the same time a recreation area for the local residents is created. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Ecology'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The response of the ecology was positive. The ecological flooding saw an increase in reeds, floodplain forest and other characteristic species of the floodplain. Typical mammal species of the floodplain also increased in the zones which were affected by ecological flooding, like the harvest mouse (Micromys minutus) which inhabits reed marches and the common shrew (Sorex araneus) and the wood mouse (Apodemus sylvat) that live in the Alder forests. The number of typical flood plain bird species also benefited from the ecological flooding. For example, the number of breeding pairs of Common Kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) increased from 4 breeding pairs in 1988 to 9 breeding pairs in 1996. Amphibians also increased in numbers between the start of Polder Altenheim as retention area in 1988 and the last monitoring event in 1996. The European tree frog (Hyla arborea), an species on the red list in Germany and a characteristic floodplain species, increased rapidly in numbers from a few individuals to 28 calling males in 1996. In 1998, the numbers increased to 100 calling males. The percentage of rheophilic fish species, Dace (Leuciscus leuciscus), Stone loach (Barbatula barbatula) and chub (Leuciscus cephalus) increased from a maximum of 5% in 1993 to 10 to 15% in 1996. The macro-invertebrates showed a positive response to the measures. The population size increased and habitats were recolonized. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ''Social-economic factors'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The ecological flooding had no negative effect on the areas outside of the floodplain and the water retention during high discharges function well. The effects on other land uses were not described in the monitoring report. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Cooperation== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The project was part of the Integriertes Rheinprogramm and was constructed by Wasser-und Schifffahrtsamt Freiburg in cooperation with Landes Baden-Württemberg | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Communication== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The communication strategy of Polder Altenheim could not be found in the available documents | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Funding== | ||
| + | |||
| + | The total costs of building the controlled inlets and the ecological monitoring were 28 million Euro which was financed by the Federal State and the National government. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Contact== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Name: Bernhard Lonsdorfer | ||
| + | |||
| + | Role: Projektingenieur | ||
| + | |||
| + | Organization Name: Regierungspräsidium Freiburg | ||
| + | |||
| + | Organization Type: Verwaltung eines Bundeslandes | ||
| + | |||
| + | Phone-Number: +49 781 933 1689 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Email: bernhard.lonsdorfer@rpf.bwl.de | ||
| − | |||
==References== | ==References== | ||
| + | |||
| + | LFU GWD (1999) Auswirkungen de Okologischen Flutungen der Polder Altenheim – Ergebnisse der Untersuchungsprogramms 1993-1996, Landesanstalt fur Umweltschutz Baden-Württemberg, Materialien zum Integrierten Rheinprogramm Band 9 | ||
| + | |||
| + | Siepe, A. (2006) Dynamische Uberflutungen am Oberrhein: Entwicklungs-Motor fur die Auwald Fauna, WGS Baden-Württemberg 10, 149-158 | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Website== | ||
| + | |||
| + | [http://www.rp-freiburg.de/servlet/PB/menu/1188090/index.html Website Integriertes Rheinprogramm (German)] | ||
<references/> | <references/> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:30, 6 August 2013
Rhine - Polder Altenheim
General description
Polder Altenheim is a 520 ha floodplain in the Upper Rhine (Rhine km 278 till 284) near the village of Altenheim. The floodplain has functioned as a controlled water retention area since 1987. Later, ecological flooding was introduced to restore the flood plain nature. 65 days per year river water is allowed to enter Polder Altenheim. It is now one of the oldest natural flood protection projects in Europe
Pressures and Drivers
The Upper Rhine suffers from hydrological regime modifications by artificial barriers upstream and downstream of Polder Altenheim. These barriers, along with channelization and embankments were built in order to control flooding of settlements in the floodplains of the Upper Rhine and for generating hydropower. The weirs now have a negative effect on the flood protection, since they impound the river blocking the discharge during high water events.
Global objectives
The global objectives were two sided. First, the projects initial goal was to restore the flood water retention capacity of the Upper Rhine to pre-weir conditions. Later, the restoration of typical Rhine floodplain nature in Polder Altenheim was added as global objective.
Specific objectives
The specific objectives for Polder Altenheim could not be found in the project documents and the question was not answered by the project manager in time. There are possible objectives for flood protection as well as some ecological targets concerning habitats, but this remains uncertain.
Success Criteria
No success criteria were mentioned in the project documents.
Site description
Measures selection
To improve the water retention capacity while retaining a natural flooding frequency, two polders (Altenheim II and Altenheim I) are connected to the main river by a controlled inlet. These inlets are designed to flood parts of the polders 65 days per year. When there is a higher discharge of once per 10 years, the polders will automatically flood to increase the retention capacity of the river. The outlet of Polder Altenheim I is connected to the retention area, Kulturwehr Kehl/Straßburg. In the polder, the dynamics caused by the ecological flooding are allowed to shape the habitats.
Monitoring
Pre-restoration monitoring
No evidence for pre-restoration monitoring could be found in the project documents
Post-restoration monitoring
In 1993 till 1996, a large monitoring program was carried out in Polder Altenheim. In this program, the quantitative changes of reeds and forests, the number of species and presence of species of macro-invertebrates (Carabidae, land snails, spiders, grasshoppers, bees, female mosquitos), the number of caught fish, the number of caught individuals of birds, small mammals and amphibians and number of breeding pairs of birds, the total flooded area in different discharge scenarios and changes in characteristics of the soil and groundwater were measured from 1993 till 1996.
Expectations and Response
It was expected that the ecological flooding regime has a positive effect on the floodplain habitats. The flood retention capacity of the Upper Rhine is enlarged and at the same time a recreation area for the local residents is created.
Ecology
The response of the ecology was positive. The ecological flooding saw an increase in reeds, floodplain forest and other characteristic species of the floodplain. Typical mammal species of the floodplain also increased in the zones which were affected by ecological flooding, like the harvest mouse (Micromys minutus) which inhabits reed marches and the common shrew (Sorex araneus) and the wood mouse (Apodemus sylvat) that live in the Alder forests. The number of typical flood plain bird species also benefited from the ecological flooding. For example, the number of breeding pairs of Common Kingfisher (Alcedo atthis) increased from 4 breeding pairs in 1988 to 9 breeding pairs in 1996. Amphibians also increased in numbers between the start of Polder Altenheim as retention area in 1988 and the last monitoring event in 1996. The European tree frog (Hyla arborea), an species on the red list in Germany and a characteristic floodplain species, increased rapidly in numbers from a few individuals to 28 calling males in 1996. In 1998, the numbers increased to 100 calling males. The percentage of rheophilic fish species, Dace (Leuciscus leuciscus), Stone loach (Barbatula barbatula) and chub (Leuciscus cephalus) increased from a maximum of 5% in 1993 to 10 to 15% in 1996. The macro-invertebrates showed a positive response to the measures. The population size increased and habitats were recolonized.
Social-economic factors
The ecological flooding had no negative effect on the areas outside of the floodplain and the water retention during high discharges function well. The effects on other land uses were not described in the monitoring report.
Cooperation
The project was part of the Integriertes Rheinprogramm and was constructed by Wasser-und Schifffahrtsamt Freiburg in cooperation with Landes Baden-Württemberg
Communication
The communication strategy of Polder Altenheim could not be found in the available documents
Funding
The total costs of building the controlled inlets and the ecological monitoring were 28 million Euro which was financed by the Federal State and the National government.
Contact
Name: Bernhard Lonsdorfer
Role: Projektingenieur
Organization Name: Regierungspräsidium Freiburg
Organization Type: Verwaltung eines Bundeslandes
Phone-Number: +49 781 933 1689
Email: bernhard.lonsdorfer@rpf.bwl.de
References
LFU GWD (1999) Auswirkungen de Okologischen Flutungen der Polder Altenheim – Ergebnisse der Untersuchungsprogramms 1993-1996, Landesanstalt fur Umweltschutz Baden-Württemberg, Materialien zum Integrierten Rheinprogramm Band 9
Siepe, A. (2006) Dynamische Uberflutungen am Oberrhein: Entwicklungs-Motor fur die Auwald Fauna, WGS Baden-Württemberg 10, 149-158
Website
Website Integriertes Rheinprogramm (German)
Related Measures
- Improve water retention
- Increase flood frequency and duration in riparian zones or floodplains
- Link flood reduction with ecological restoration
- Construct semi-natural/articificial wetlands or aquatic habitats